DCOM Configuration for OPC
What is DCOM?
DCOM is a Microsoft technology and it stands for Distributed Component Object Model.
It is used for RPC (Remote Procedure Call) systems to enable communication between COM-based
applications over the network.
Why is it important for OPC Classic?
All OPC DA (Data Access), A&E (Alarms & Events), and HDA (Historical Data Access) communication
is based on COM and DCOM. OPC clients and servers
use COM to communicate with each other over the same machine and use DCOM to communicate directly with each other across a network.
FAQs and Common DCOM problems:
Because DCOM security is such a common concern it can cause communication problems for
implementers of OPC systems, as it restricts the use of OPC technology to Windows operating systems.
A certain amount of configuration is required on the system where the OPC server is installed to
allow remote clients to connect to it over the network.
To properly to configure COM/DCOM to connect an OPC client to an OPC Server and your DEP,
specific DCOM troubleshooting guides can be found here:
Still having connectivity issues?
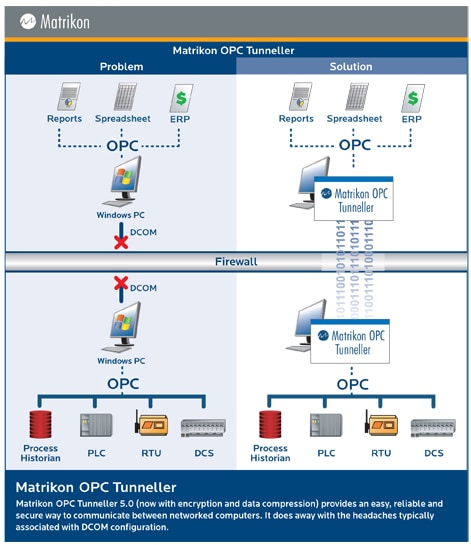
Products such as Matrikon OPC Tunneller
offer another route to bypassing DCOM. In this case, Tunneller is installed on both client and server PCs,
interfacing with the true OPC client and server via local COM. The two copies of Tunneller then communicate
with one another using one of a number of supported protocols, including TCP/IP.
More Information: